National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Magnet Academy: Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi was a titan of twentieth-century physics. He outlined the statistical laws that govern the behavior of particles that abide by the Pauli exclusion principle and developed a theoretical model of the atom in his mid-twenties....
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
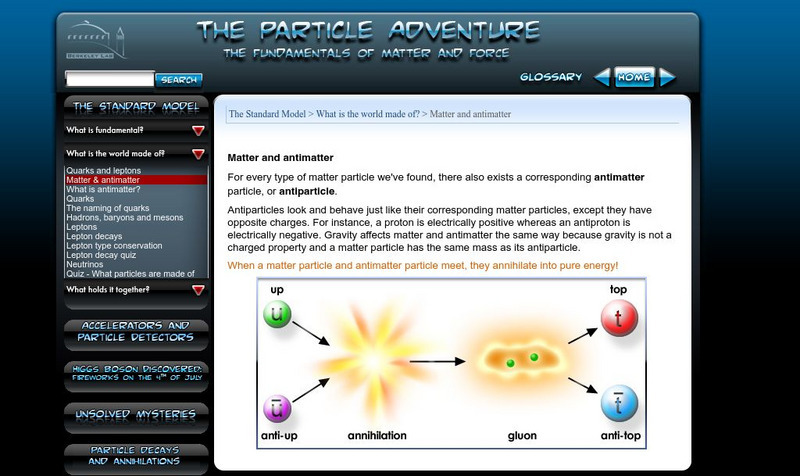
Berkeley Lab: Particle Adventure: Matter and Antimatter
The beginning of an informative tutorial on antimatter, covering quarks, hadrons, baryons, mesons, leptons, and neutrinos.
Wikimedia
Wikipedia: Ferromagnetism
This site from Wikipedia provides a wonderful in-depth explanation of ferromagnetism, covering the atomic behavior which is responsible for ferromagnetic properties. Also introduces the concepts of magnetic domains and the Curie...
Concord Consortium
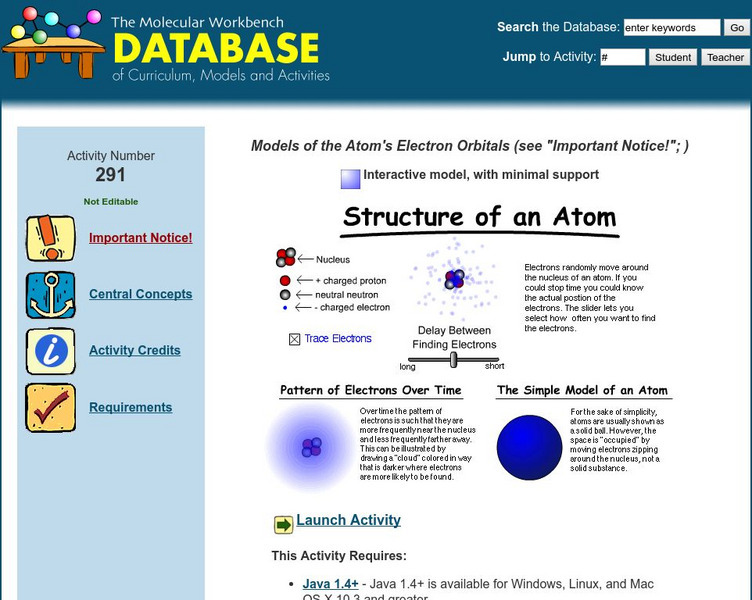
The Molecular Workbench Database: Models of the Atom's Electron Orbitals
Learn about atomic structure and the multiple theories of atomic structure in this simulation.
Other
Sir Joseph John Thomson
Have you ever wondered who discovered the electron? The answer is Nobel Prize winning physicist Sir Joseph John Thomson.
Friesian School
Proceedings of the Friesian School/the Quantacized Atom
A very lengthy page from friesian.com discussing Bohr's theory of electronic energy levels and the explanation of commonly observed atomic emission line spectra. The concept of a photon and Einstein's observation of the photoelectric...
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Berkeley Lab: Particle Adventure: The Standard Model
An introduction to the Standard Model, a theory which attempts to explain atomic structure using leptons, quarks, and force carrier particles.
University of St. Andrews (UK)
University of St. Andrews: Insulators
The nature of insulators is described at the atomic level. Band gap theory is used to explain what distinguishes insulators from conductors.